Each type of osteoarthritis occurs with degenerative and dystrophic processes in the articular tissue. The disease is always chronic and is not completely cured, you can only slow down or stop its development.
According to ICD-10, gonarthrosis (damage to the knee joints) belongs to the group under the code "M17". In the treatment, the emphasis is on drug treatment, surgical intervention is used only when the course develops.
What happens to the knee joint with osteoarthritis?
Osteoarthritis of the knee joint is accompanied by degenerative and dystrophic processes, if left untreated, progresses steadily. In this case, except in rare cases, inflammatory processes are not observed.
Joint degeneration and dystrophy have virtually no effect on knee function. Over time, these processes lead to the disruption of the structure of the joint, stop "sliding", the formation of bubbles on the surface (due to deformation changes).
Blood circulation decreases, local metabolism (metabolic processes) deteriorates, which only increases the course of the disease. The process of degeneration of hyaline cartilage begins very quickly, thinning, stratification, and then the appearance of cracks on it.
The end result of the disease is the complete destruction of the hyaline cartilage by exposure to the adjacent bone. But the problem doesn't end there: the latter begins to thicken due to exposure to the bone, and bone growths appear on it (often in the form of thorns).
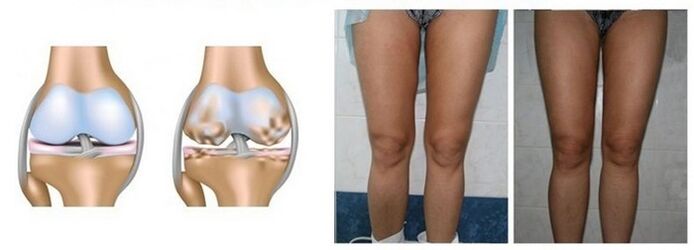
All this causes the affected joint to deform and then bend. That is why the disease is called "deforming arthrosis". With an existing deformity of the muscle, the disease cannot be treated without surgery.
Causes of the disease
Often, several predisposing factors appear before the development of osteoarthritis of the knee. It is not necessary to have congenital risk factors, the disease often develops due to acquired factors (trauma, infection, inflammation).
The main reasons:
- Serious disorders of metabolic / metabolic processes in the body (any acute or chronic severe diseases of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands).
- Circulatory disorders and a tendency to capillary bleeding (due to fragility).
- Excess weight with a significant increase in the load on the musculoskeletal system (obesity stage II-III).
- Damage to the knee joints (including direct injuries, penetrating wounds, rupture of the garden apparatus, damage to the meniscus, fractures, dislocations and subluxations, cracks).
- Inflammatory pathologies (primarily arthritis or rheumatism) that have suffered in the recent past.
- Excessive physical activity (risk group includes athletes, gymnasts, people playing tennis, football, basketball).
- Consequences of long-term, poorly treated knee injury.
- Congenital defects and anomalies in the structure of articular tissues, hereditary risk factors (genetic mutations).
There is a direct link between the cause and severity of osteoarthritis. If it is caused by metabolic disorders or severe injuries, the prognosis is worse than the development of osteoarthritis against the background of joint overload or age-related dystrophic changes.
Disease statistics
According to statistics, osteoarthritis of the knee joint is very common; generally occupies one of the leading positions among all forms of osteoarthritis. About 20% of patients who go to private medical institutions suffer from gonarthrosis.
Taking into account all diseases of the knee joints, the share of osteoarthritis among them is about 53%. Recently, especially in developed countries, there has been an increase in the number of cases of gonarthrosis among the population.
This is due to an increase in life expectancy (the older a person is, the greater the risk of this form of osteoarthritis) and the predominance of a sedentary lifestyle. And this is really a problem, because doctors still can not completely cure gonarthrosis.
Why is gonarthrosis dangerous?
The main danger of gonarthrosis is disability due to the development of complications that are not suitable for conservative treatment. First of all, it is a deformation of the joint and bone of the affected joint. Disability is already possible in the third stage of the disease.
The second danger is the development of chronic severe pain that can disturb the patient beyond his normal sleep. Constant arousal due to knee pain is one of the most common problems of stage 3-4 gonarthrosis.
There are no fatal consequences due to gonarthrosis. Theoretically, a serious injury can occur due to sudden joint blockage. This is the so-called symptom of joint blockade, which is most often observed in stages 3-4 of the disease.
The degree of gonarthrosis and the difference between them
The disease is divided into four stages, which differ according to the severity of the course, the severity and number of symptoms and the final prognosis. In addition, each stage of osteoarthritis is treated differently (although differences in treatment regimens may seem small to non-physicians).
Degree of gonarthrosis:
- first degree: the disease does not manifest itself in virtually any way, only a small discomfort is possible, but in general the patient feels well, and therefore it is very difficult to diagnose the disease at an early stage;
- second degree: severe painful sensations appear, especially after a long walk or leg; develops a characteristic crisis during physical activity, the process of atrophy of the quadriceps femur muscle may already begin;
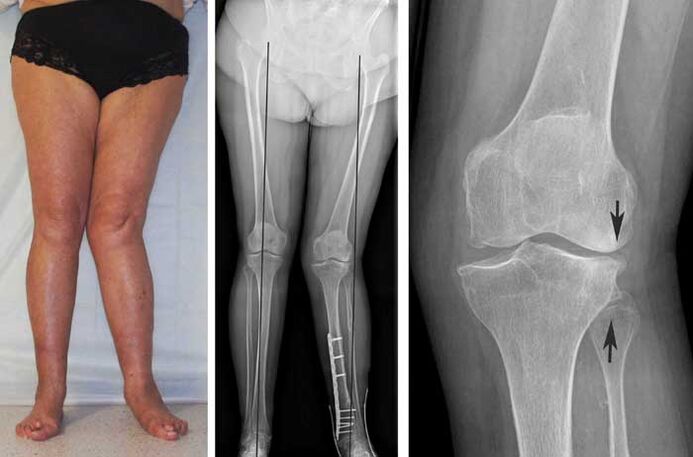
- third degree: the pain becomes unbearable, the patient is constantly anxious, there are serious deformity changes in the joint, it becomes warm to the touch, it is impossible to walk normally or run more;
- fourth degree: very difficult with severe deformities of the joint and constant pain that does not even allow the patient to sleep; joint dysfunction is so obvious that ankylosis is possible (complete immobilization of the affected joint).
The first two degrees of gonarthrosis are considered conditionally favorable because they do not interfere with a person's normal life. The last two stages are very severe and lead to disability.
Symptoms at different stages of gonarthrosis
The clinical picture of gonarthrosis depends on the stage of the disease. In the first stage, there may be no symptoms, and in the fourth stage, it is very clear and does not stop bothering the patient, even under strong drug treatment.
Stage 1 symptoms:
- A little discomfort or pain with severe stress in the joint.
- Very little noticeable crunch.
- A slight increase in the size of the joint.
Stage 2 symptoms:
- moderate to severe pain, usually with a period of exacerbation and remission;
- the joint becomes hot to the touch;
- redness of the skin is possible on the affected joint;
- moderate knee dysfunction (walking and running are still possible, but with some difficulty);
- increased pain in the morning and after standing for a long time.
Stage 3 symptoms:
- severe pain that bothers the patient day and night, but during the period of inflammation (triggers for inflammation for each patient) the pain intensifies several times;
- visible deformity changes in the knee, increase in size;
- redness on palpation of the affected joint;
- normal movement is impossible due to partial immobilization of the joint;
- probably the curvature of the lower leg.
Stage 4 symptoms:
- pain becomes unbearable, does not allow the patient to engage in daily activities (including intellectual work, because pain impairs cognitive function);
- appearance of synovitis due to accumulation of effusion in the cavity of the knee cartilage;
- now the deformity changes are already evident not only in the joint but also in the extremity as a whole;
- sensation of fluctuations during palpation of the patella and surrounding tissues;
- almost complete or even complete immobilization of the knee joint (in this case, only surgery will help to restore the functionality of the joint).
If it is not possible to eliminate or significantly reduce the pain in stage 3-4 of osteoarthritis, doctors resort to analgesic blockades, but blockages can not be done every day.
Diagnostics
In the diagnosis of knee osteoarthritis, the emphasis is on imaging techniques, and laboratory tests generally show nothing.
Diagnostic methods used:
- Examination by an orthopedist with palpation of the affected joint, linear measurements of bones, angiometry.
- Clinical blood tests (total and erythrocyte sedimentation rate / ESR), determination of fibrinogen levels in the blood and urine and, above all, urea and other biochemical parameters.
- Radiography (narrowing of the joint space, deformities, cartilage sclerosis, accumulation of salts and even bone osteophytes are detected).
- Ultrasound examination (for differential diagnosis only).
- Magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography (imaging is the most informative in terms of diagnostic methods).
Generally, an X-ray is sufficient to make a diagnosis, especially if the disease is advanced. Relatively rarely, computed or magnetic resonance imaging is required.
Treatment of gonarthrosis: methods
The treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee is only complicated because no treatment is better than others (even medications). The treatment is long-lasting, can last for years, and is sometimes prescribed for the rest of your life.
Methods of treatment used:
- drug treatment - the basis of treatment;
- physiotherapy exercises;
- diet therapy;
- physiotherapy treatment;
- surgical intervention.
The main thing in the treatment of osteoarthritis is the systematic nature of the process and the unconditional adherence to the recommendations of the attending physician. Attempts to treat gonarthrosis independently, including disregarding a doctor's prescription, result in disability.
Exercise therapy
Physiotherapy exercises are most suitable for the treatment of 1-2 stages of osteoarthritis of the knee joints. At such stages, this is almost the main method of treatment, because physical training can slow the progression of the disease and eliminate most of the symptoms.
However, classical physical education has no special meaning and can be harmful. Therefore, the patient is prescribed special exercises and individually (because gonarthrosis can go differently in individual patients).
There is no time for treatment with exercise therapy methods - ideally, you should visit a doctor from time to time for dynamic monitoring of the joint and engage in lifelong prescribed exercises. It is very useful to combine exercise therapy with exercises in the pool (there is very little load on the joints).
Diet
Although nutritional correction may be very helpful, it is not a mandatory treatment. In only 40% of cases, dietary treatment gives noticeable results and generally gives the onset of osteoarthritis in people with endocrine pathologies.
The patient is instructed to avoid fatty, fried, salty and smoked foods. The use of alcohol is prohibited, and sometimes smoking is prohibited. At the same time, the consumption of large amounts of vegetables, fruits and meat products is determined.
In this case, it can not be called sausage, sausage or strained meat products. The patient is instructed to eat lean meat, boiled chicken is especially useful (due to its relatively low calorie and high protein content).
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy procedures are useful not only in terms of relieving the symptoms of osteoarthritis, but also do not directly affect the disease. That is, no matter what some "experts" say there, it is impossible to treat even the first stage of osteoarthritis with the help of physiotherapy.
Physiotherapy is good for relieving pain, but only if it is mild. With severe pain (stages 3-4 of osteoarthritis), physiotherapy will not help, as well as most medications (especially for oral use).
The most popular treatments for osteoarthritis are magnetotherapy, quantum therapy, mud therapy, acupuncture and hirudotherapy (leech therapy). Shock physical therapy is prohibited due to the risk of additional joint damage.
Operation
Surgery is required only in stages 3-4 of the disease, when conservative methods are not needed. Different types of procedures can be used: drainage of the joint cavity, removal of bone osteophytes, replacement of the joint (prosthesis).
Transplantation is best to restore the functionality of the joint, but the problem is a very expensive procedure. As a result, only 10-15% of patients can afford such an operation. But even with the right amount of money, it is not always possible to change the combination.
The fact is that such a procedure is contraindicated in patients with severe conditions or in patients over 65-70 years. Remember that each knee operation has its own risk of complications (even fatal complications are possible, but very rare).
Medication
Along with physiotherapy exercises, it is the basis of treatment and its mandatory component. If other procedures are still not available, it is not possible to do without medication in combination with exercise therapy (traditional medicine cannot replace medication).
The patient is prescribed painkillers (with severe pain - blockade), decongestants, muscle relaxants, antihistamines. Chondroprotectors are often prescribed, injections of hyaluronic acid are possible (replaces the physiological lubrication of the joints).
Medications can affect the disease only in stages 1-2 of osteoarthritis. In stage 3-4 of the disease, drug treatment only plays the role of a method of combating symptoms, nothing but surgery can affect the disease.
Nuances of treatment in the stage of exacerbation and remission
Approaches to the treatment of knee osteoarthritis during exacerbation and remission are somewhat different. In the acute phase, aggressive therapy is used to restore joint function as quickly as possible and relieve symptoms.
The pain reaches its peak during the exacerbation of the disease, so in such cases, drug blockade may be prescribed.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may be prescribed. Although osteoarthritis generally persists without inflammation, it can occur in an acute stage. The patient is prescribed bed rest, minimal stress on the affected joint and prevention of overheating of the joint.
On the contrary, during the remission phase, physical exercise is prescribed and an increase in physical activity is generally prescribed. This is because the joint function improves in remission and the pain is generally of moderate intensity.
Remission should be used skillfully - this is a time when swimming lessons, lessons with a rehabilitation therapist and attempts to restore joint functionality are possible. You can't do without medication at this stage.
Often, chondroprotectors, oral painkillers are prescribed (at the patient's request, because if the pain is difficult to notice, there is no need to take them). Ointments, gels and creams can be prescribed, including those that have a warming effect (it is better not to use them during inflammation).
In addition, massage, including hand therapy, may be prescribed (only if the disease is in stage 1-2). Special gymnastics techniques can be used with a doctor's permission.
Remission is an ideal time for physiotherapy, but the choice of specific physiotherapy should be made by the doctor, not the patient. Finally, if necessary, injections of hyaluronic acid may be given during remission.
Hyaluronic acid is not prescribed with exacerbation of osteoarthritis, because such an injection against the background of inflammation will lead to serious consequences. Note: Injections should only be performed by a qualified professional.
Ordinary doctors and even nurses (paramedics, nurses) are not allowed to inject such needles. Self-injection is fraught not only with disability but also with death (due to the risk of anaphylactic shock or blood clots if the needle accidentally enters a vein).
Treatment prognosis
The prognosis of gonarthrosis varies depending on the stage of the disease and the patient's general health. If this is stage 1-2 and treatment is started immediately, the prognosis is very favorable, especially in able-bodied people.
The prognosis is extremely poor in both young patients and the elderly with stage 3-4 osteoarthritis. Although it has been found that young people are more tolerant of osteoarthritis at such stages, it still inevitably leads to disability.
However, the presence of 3-4 stages of osteoarthritis is not equal to one sentence. In fact, with surgery, you can try to restore most, not all, functions of the knee. Artificial joint implantation can give excellent results.
Prevention of osteoarthritis of the knee joint
Osteoarthritis is a group of diseases that can be completely prevented by following simple preventive measures. Of course, such measures do not guarantee 100% protection, but they can reduce the risk of disease (especially in people at risk).
Preventive measures:
- Unnecessary stress on the joints should be avoided (such loads include professional sports).
- Rational nutrition with the predominance of fruits and vegetables in the daily diet.
- Maintain good physical shape, regular gymnastics.
- Prevention or elimination of obesity (more body weight - more stress on the joints in the body).
- Prophylactic treatment with chondroprotectors after the age of 45 (only after consulting a doctor).
- Daily fluid intake (about 1. 5 liters of water per day) minimizes salt intake.
The main thing is not to overload physical activity, because it is only moderately useful (if there is no wear and tear of the musculoskeletal system). Physical training is useful, sports are not especially useful for the joints and cardiovascular system.

























